Understanding the Role of Nutrients in the Body
Have you ever wondered how the food you consume transforms into energy, growth, and overall vitality? The secret lies in the nutrients your body absorbs from every meal. These essential compounds are the building blocks of life, playing crucial roles in maintaining health and preventing disease. Without the right balance of nutrients, our bodies would struggle to function efficiently, leading to a host of health issues. From the carbohydrates that fuel our daily activities to the vitamins that bolster our immune defenses, each nutrient serves a distinct and vital purpose. Understanding these roles can empower you to make informed dietary choices, ultimately enhancing your well-being.
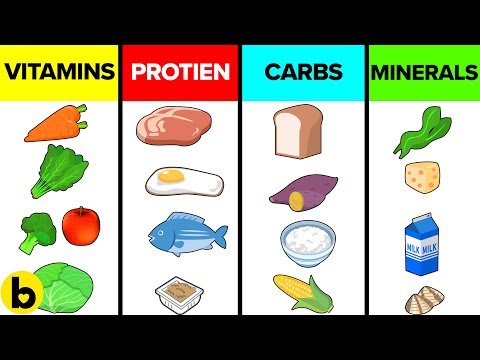
The Basics of Nutrient Functionality
Nutrients are substances obtained from food that are necessary for the maintenance of life and health. They are classified into macronutrients and micronutrients. Macronutrients, which include carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, are required in larger amounts and provide the energy needed for daily activities. Micronutrients, such as vitamins and minerals, are needed in smaller quantities but are equally crucial for bodily functions. Each type of nutrient plays a specific role, from energy production to cellular repair. For instance, carbohydrates are primarily used for energy, while proteins are essential for tissue growth and repair. Fats, on the other hand, are vital for hormone production and cell structure.
How Nutrients Support Overall Health
The overall health of an individual is intricately linked to the nutrients they consume. A balanced diet rich in essential nutrients can prevent chronic diseases, improve mental health, and enhance physical performance. Vitamins and minerals, although required in smaller amounts, are indispensable for various biochemical processes. For example, vitamin C is crucial for collagen synthesis, while iron is essential for oxygen transport in the blood. Ensuring an adequate intake of these nutrients can significantly boost your immune system, protect against oxidative stress, and support cognitive function. By understanding the diverse roles of nutrients, you can tailor your diet to meet your specific health needs.
Nutrients and Energy Production
Energy is the cornerstone of life, and nutrients are the fuel that powers it. The body converts the food we eat into energy through a complex series of biochemical reactions. This energy is then used to perform various functions, from basic metabolic processes to intense physical activities. Without a steady supply of nutrients, the body would be unable to sustain its energy demands, leading to fatigue and decreased performance.
Carbohydrates as a Primary Energy Source
Carbohydrates are the body’s preferred source of energy. They are broken down into glucose, which is then used by cells to produce ATP, the energy currency of the body. Simple carbohydrates, like sugars, provide quick energy, while complex carbohydrates, such as starches, offer a more sustained release. Incorporating a mix of both can help maintain energy levels throughout the day. However, it’s important to choose whole grains and fiber-rich sources to avoid spikes in blood sugar levels.
The Role of Fats in Energy Storage and Utilization
Fats are a concentrated source of energy, providing more than twice the calories per gram compared to carbohydrates and proteins. They are stored in adipose tissue and can be mobilized when energy demands increase. Fats also play a critical role in the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins and the production of essential fatty acids. Incorporating healthy fats, such as those from avocados and nuts, can support energy balance and overall health. It’s crucial to limit saturated and trans fats, which can contribute to cardiovascular disease.
Nutrients for Growth and Development
Growth and development are fundamental aspects of life, and nutrients are the key drivers of these processes. From infancy through adulthood, the body requires a steady supply of nutrients to build and repair tissues, support organ function, and facilitate growth. A lack of essential nutrients during critical growth periods can lead to developmental delays and long-term health issues.
Proteins and Their Role in Tissue Building
Proteins are the building blocks of the body, composed of amino acids that are essential for the growth and repair of tissues. They are involved in the formation of muscles, skin, hair, and nails, as well as the production of enzymes and hormones. Adequate protein intake is crucial for maintaining muscle mass and supporting recovery after exercise. Animal-based proteins, such as meat and dairy, provide complete amino acids, while plant-based sources, like beans and lentils, can be combined to achieve a complete profile.
Essential Vitamins and Minerals for Growth
Vitamins and minerals play a pivotal role in growth and development. Calcium and vitamin D are essential for bone growth, while iron is crucial for cognitive development and oxygen transport. Zinc supports immune function and cell growth, and vitamin A is vital for vision and skin health. Ensuring a diverse diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can provide these essential nutrients. Supplements may be necessary in cases of deficiency, but it’s always best to consult a healthcare professional before starting any supplementation.
Nutrients in Immune System Support
The immune system is the body’s defense mechanism against infections and diseases, and nutrients are vital in maintaining its strength and resilience. A well-nourished immune system can effectively combat pathogens and reduce the risk of illness. Key nutrients, such as vitamins and minerals, play specific roles in immune function, from enhancing the production of immune cells to neutralizing harmful free radicals.
How Vitamins Boost Immunity
Vitamins are essential for a robust immune response. Vitamin C, for instance, is known for its role in enhancing the production of white blood cells, which are crucial for fighting infections. Vitamin D modulates the immune response and has been linked to a reduced risk of respiratory infections. Incorporating a variety of fruits and vegetables can provide these vital vitamins and support immune health. It’s important to note that while supplementation can be beneficial, it should not replace a balanced diet.
The Importance of Minerals in Immune Function
Minerals, such as zinc and selenium, are also critical for immune function. Zinc plays a role in the development and function of immune cells, while selenium has antioxidant properties that help protect cells from damage. Ensuring adequate intake of these minerals can enhance the body’s ability to ward off infections. Foods rich in zinc include meat, shellfish, and legumes, while selenium can be found in nuts, seeds, and whole grains.
Nutrients and Brain Health
The brain is an intricate organ that requires a constant supply of nutrients to function optimally. These nutrients not only support cognitive processes but also protect against neurological disorders. A diet rich in essential nutrients can enhance memory, concentration, and overall mental well-being. Understanding which nutrients are beneficial for brain health can help you make informed dietary choices.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Cognitive Function
Omega-3 fatty acids, particularly DHA and EPA, are crucial for brain health. They are integral components of cell membranes in the brain and play a role in neurotransmitter function. Studies have shown that omega-3s can improve cognitive function, reduce inflammation, and lower the risk of neurodegenerative diseases. Incorporating fatty fish, such as salmon and mackerel, into your diet can provide these essential fatty acids. For those who do not consume fish, flaxseeds and walnuts are excellent plant-based alternatives.
The Impact of Micronutrients on Mental Health
Micronutrients, including vitamins and minerals, are vital for maintaining mental health. B vitamins, such as B6, B12, and folate, are involved in neurotransmitter synthesis and can influence mood and cognitive function. Deficiencies in these vitamins have been linked to depression and cognitive decline. Ensuring adequate intake of B vitamins through whole grains, leafy greens, and fortified cereals can support mental health. Additionally, minerals like magnesium and zinc are important for brain function and have been associated with reduced anxiety and improved mood.
Nutrients for Bone and Muscle Health
Strong bones and muscles are essential for overall health and mobility. Nutrients play a pivotal role in maintaining bone density and muscle mass, especially as we age. A diet rich in calcium, vitamin D, and protein can support bone and muscle health, reducing the risk of fractures and muscle loss.
Calcium and Vitamin D for Strong Bones
Calcium is a major component of bone tissue, and adequate intake is necessary for maintaining bone strength. Vitamin D enhances calcium absorption and is crucial for bone health. A deficiency in either nutrient can lead to weakened bones and an increased risk of osteoporosis. Dairy products, leafy greens, and fortified foods are excellent sources of calcium. Sunlight exposure and fortified foods can provide vitamin D, but supplements may be necessary in regions with limited sunlight.
Protein and Magnesium in Muscle Maintenance
Protein is essential for muscle repair and growth. It provides the amino acids needed to build and maintain muscle tissue. Magnesium plays a role in muscle contraction and relaxation, and its deficiency can lead to muscle cramps and weakness. Incorporating lean meats, beans, and nuts into your diet can provide the protein and magnesium necessary for muscle health. It’s important to balance protein intake with regular physical activity to maintain muscle mass.
Nutrients and Digestive Health
Digestive health is crucial for nutrient absorption and overall well-being. Nutrients, particularly fiber and probiotics, play a significant role in maintaining a healthy digestive system. A diet that supports digestive health can prevent gastrointestinal issues and promote regular bowel movements.
The Role of Fiber in Digestion
Fiber is a type of carbohydrate that the body cannot digest. It adds bulk to the stool and aids in regular bowel movements, preventing constipation. Soluble fiber, found in oats and legumes, can help lower cholesterol levels, while insoluble fiber, found in whole grains and vegetables, promotes gut health. Ensuring a diet rich in both types of fiber can support digestive health and reduce the risk of digestive disorders.
Probiotics and Gut Health
Probiotics are live bacteria that provide health benefits when consumed. They help maintain a healthy balance of gut flora, which is essential for digestion and immune function. Fermented foods, such as yogurt, kefir, and sauerkraut, are excellent sources of probiotics. Incorporating these foods into your diet can enhance gut health and improve digestion. While probiotic supplements are available, it’s best to obtain them from natural food sources whenever possible.
Nutrients in Disease Prevention
A nutrient-rich diet can play a significant role in preventing chronic diseases. Antioxidants and phytochemicals, found in various foods, offer protective effects against oxidative stress and inflammation, both of which are linked to numerous health conditions. Understanding the role of these nutrients can empower you to make dietary choices that support long-term health.
Antioxidants and Their Protective Effects
Antioxidants are compounds that neutralize free radicals, reducing oxidative stress and cellular damage. Vitamins C and E, along with beta-carotene, are well-known antioxidants that protect against chronic diseases such as heart disease and cancer. Fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds are rich sources of antioxidants. Incorporating a variety of these foods into your diet can provide the necessary protection against oxidative damage.
The Role of Phytochemicals in Reducing Disease Risk
Phytochemicals are naturally occurring compounds found in plants that have health-promoting properties. They include flavonoids, carotenoids, and polyphenols, which have been linked to reduced risks of chronic diseases. These compounds exhibit anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects, supporting overall health. Consuming a diverse range of colorful fruits and vegetables can provide a wide array of phytochemicals. This dietary diversity is key to harnessing the full benefits of these powerful compounds.
Common Pitfalls and Mistakes in Nutrient Intake
Despite the importance of nutrients, many individuals fall short in their dietary intake, leading to deficiencies and health issues. Understanding common pitfalls can help you avoid these mistakes and ensure a balanced diet.
One common mistake is relying heavily on processed foods, which are often low in essential nutrients and high in unhealthy fats and sugars. Opting for whole, unprocessed foods can significantly improve nutrient intake. Another pitfall is neglecting hydration, as water is crucial for nutrient transport and metabolism. Ensuring adequate water intake is as important as consuming a balanced diet.
Many people also overlook the importance of dietary variety. Consuming a limited range of foods can lead to nutrient deficiencies. Incorporating a diverse array of foods can provide a more comprehensive nutrient profile. Additionally, portion control is essential, as overeating can lead to nutrient imbalances and weight gain. Being mindful of portion sizes can help maintain a healthy diet.
Finally, some individuals may rely too heavily on supplements, believing they can replace a healthy diet. While supplements can be beneficial in certain cases, they should not substitute for nutrient-rich foods. Consulting with a healthcare professional can help determine if supplementation is necessary.
Unlocking the Secrets: How Your Body Utilizes Nutrients
What are the primary functions of nutrients in the body?
Nutrients play a crucial role in the body by providing energy, supporting growth and development, maintaining and repairing tissues, and regulating various bodily processes.
How do carbohydrates influence your energy levels?
Carbohydrates are the body’s main source of energy. They are broken down into glucose, which fuels cells, tissues, and organs, especially during physical activity.
Why are proteins essential for muscle health?
Proteins are vital for building and repairing muscle tissues. They provide the amino acids necessary for muscle growth, maintenance, and recovery after exercise.
What role do vitamins and minerals play in maintaining health?
Vitamins and minerals are essential for numerous bodily functions, including immune support, bone health, and converting food into energy. They also help in wound healing and maintaining healthy skin.
How do fats contribute to nutrient absorption?
Fats are necessary for absorbing fat-soluble vitamins like A, D, E, and K. They also provide essential fatty acids that the body cannot produce on its own.
In what ways do nutrients support the immune system?
Nutrients such as vitamins C and D, zinc, and antioxidants help strengthen the immune system by supporting the production and function of immune cells, reducing inflammation, and protecting against infections.
How do nutrients affect brain function and mental health?
Nutrients like omega-3 fatty acids, B vitamins, and iron are crucial for brain health. They support cognitive function, improve mood, and may reduce the risk of mental health disorders.
Can a nutrient deficiency impact overall health?
Yes, nutrient deficiencies can lead to various health problems, including weakened immunity, poor bone health, fatigue, and impaired growth and development. It’s essential to maintain a balanced diet to prevent deficiencies.