Understanding Vitamin A and Its Importance
Have you ever wondered why carrots are often touted as the ultimate eye food? The secret lies in their rich content of Vitamin A, a crucial nutrient for maintaining optimal health. This vitamin plays a pivotal role in various bodily functions, yet its deficiency is alarmingly common in many parts of the world. Understanding the significance of Vitamin A can be the first step in preventing serious health issues. Let’s delve into what makes this vitamin so essential and explore the consequences of its deficiency.
What is Vitamin A?
Vitamin A is a fat-soluble vitamin that is vital for numerous physiological processes. It exists in two primary forms: preformed Vitamin A, found in animal products, and provitamin A carotenoids, present in plant-based foods. The body converts these carotenoids into retinol, an active form of Vitamin A. This nutrient is stored in the liver and released into the bloodstream as needed, ensuring a steady supply to various tissues.
Functions of Vitamin A in the Body
The functions of Vitamin A are diverse and critical. It is indispensable for maintaining healthy vision, particularly in low-light conditions. Additionally, it supports the immune system by enhancing the function of white blood cells, which are essential for fighting infections. Vitamin A also plays a role in cell growth and differentiation, making it crucial for skin health and the maintenance of mucous membranes. Furthermore, it contributes to reproductive health and fetal development, highlighting its importance across all stages of life.
Sources of Vitamin A
To meet the body’s needs for Vitamin A, it’s important to consume a balanced diet that includes both animal and plant sources. Animal products like liver, fish oils, and dairy are rich in preformed Vitamin A. On the other hand, colorful fruits and vegetables, such as carrots, sweet potatoes, and spinach, are excellent sources of provitamin A carotenoids. Incorporating a variety of these foods into your diet can help ensure adequate intake of this vital nutrient.
The Role of Vitamin A in Eye Health
Vision is one of the most cherished senses, and Vitamin A is integral to maintaining it. This nutrient is a key component of rhodopsin, a protein in the eyes that absorbs light and supports vision in dim lighting. Without sufficient Vitamin A, the eyes struggle to adjust to darkness, leading to night blindness. Let’s explore how this vitamin supports eye health and the consequences of its deficiency.
How Vitamin A Supports Vision
Vitamin A is essential for the production of rhodopsin, which is located in the retina. Rhodopsin enables the eyes to detect light and transmit signals to the brain, allowing us to see in low-light conditions. In addition to supporting night vision, Vitamin A helps maintain the cornea, the eye’s outermost layer, ensuring it remains clear and healthy.
Symptoms of Vitamin A Deficiency in Eyes
When the body lacks sufficient Vitamin A, the eyes are among the first organs to show symptoms. Initial signs include difficulty seeing in dim light, a condition known as night blindness. If the deficiency persists, it can lead to more severe issues like xerophthalmia, characterized by dryness and thickening of the cornea. In extreme cases, prolonged deficiency can result in complete vision loss.
Preventing Night Blindness
Preventing night blindness involves ensuring adequate intake of Vitamin A through diet or supplements. Consuming foods rich in this nutrient can help maintain healthy levels and prevent the onset of deficiency-related vision problems. Regular eye check-ups can also aid in early detection and management of any issues related to Vitamin A deficiency.
Identifying Vitamin A Deficiency
Recognizing the signs of Vitamin A deficiency is crucial for timely intervention and treatment. This deficiency can manifest in various ways, affecting not only vision but also other aspects of health. Understanding who is at risk and how to diagnose this condition can help prevent its adverse effects.
Common Signs and Symptoms
The symptoms of Vitamin A deficiency extend beyond vision problems. Individuals may experience dry skin, frequent infections, and delayed wound healing. In children, it can lead to stunted growth and increased susceptibility to infections. Recognizing these signs early can prompt necessary dietary changes or medical interventions.
Who is at Risk?
Certain populations are more susceptible to Vitamin A deficiency. These include individuals with limited access to nutritious foods, particularly in developing countries. Pregnant and breastfeeding women, as well as young children, are also at higher risk due to increased nutritional needs. Additionally, people with conditions that impair fat absorption, such as cystic fibrosis or Crohn’s disease, may be more prone to deficiency.
Diagnosing Vitamin A Deficiency
Diagnosing Vitamin A deficiency typically involves a combination of clinical assessment and laboratory tests. Healthcare providers may evaluate symptoms and dietary history, followed by blood tests to measure retinol levels. Early diagnosis is key to preventing the progression of deficiency-related health issues. In some cases, additional tests may be conducted to assess the impact on vision and overall health.
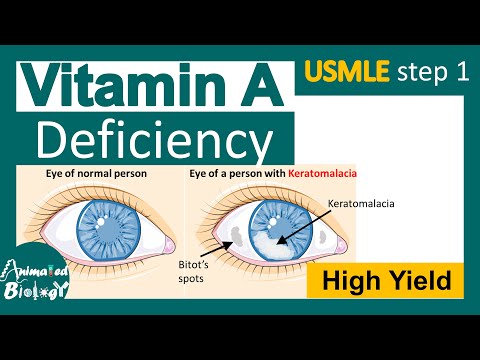
Xerophthalmia: The Disease Linked to Vitamin A Deficiency
Xerophthalmia is a severe eye condition directly associated with insufficient Vitamin A intake. This disease progresses through several stages, each with increasing severity and potential for long-term damage. Understanding xerophthalmia is crucial for preventing irreversible vision loss and maintaining eye health.
What is Xerophthalmia?
Xerophthalmia encompasses a range of eye disorders resulting from Vitamin A deficiency. It begins with night blindness and can advance to more serious conditions, such as Bitot’s spots and corneal ulcers. Without intervention, xerophthalmia can lead to permanent blindness. This condition is most prevalent in regions where malnutrition is common, highlighting the importance of nutritional education and access to Vitamin A-rich foods.
Stages of Xerophthalmia
The progression of xerophthalmia is marked by distinct stages. Initially, individuals may experience night blindness, followed by conjunctival xerosis, where the conjunctiva becomes dry and thickened. As the condition advances, Bitot’s spots, which are foamy patches on the conjunctiva, may appear. In severe cases, corneal xerosis and ulcers develop, potentially leading to corneal scarring and blindness.
Long-term Effects on Vision
Without timely treatment, xerophthalmia can have devastating effects on vision. The damage to the cornea may become irreversible, resulting in permanent vision impairment or loss. Addressing Vitamin A deficiency early can prevent these long-term consequences and preserve eye health. Public health initiatives aimed at improving nutrition and access to Vitamin A supplements are vital in combating this preventable condition.
Other Health Issues Related to Vitamin A Deficiency
Beyond its critical role in vision, Vitamin A deficiency can lead to a host of other health problems. This nutrient is integral to several bodily functions, and its absence can have widespread effects. Understanding these impacts can help in recognizing and addressing deficiency-related health concerns.
Impact on Immune Function
Vitamin A is essential for a robust immune system. It plays a pivotal role in the production and function of white blood cells, which are crucial for fighting infections. A lack of this vitamin can weaken the immune response, making individuals more susceptible to illnesses. Frequent infections and prolonged recovery times can be indicative of an underlying Vitamin A deficiency. Ensuring adequate intake of this nutrient is vital for maintaining immune health and reducing the risk of infectious diseases.
Skin and Hair Health Concerns
The health of skin and hair is closely linked to Vitamin A levels. This vitamin supports the maintenance of epithelial tissues, which include the skin and mucous membranes. A deficiency can lead to dry, flaky skin and brittle hair. In severe cases, it may contribute to conditions like hyperkeratosis, where the skin becomes thickened and rough. Incorporating Vitamin A-rich foods into the diet can help maintain healthy skin and hair, preventing these issues.
Growth and Development in Children
Vitamin A is crucial for the growth and development of children. It supports bone growth and the development of vital organs. A deficiency during childhood can lead to stunted growth and developmental delays. Ensuring that children receive adequate amounts of this nutrient is essential for their overall health and well-being. Parents and caregivers should focus on providing a balanced diet that includes sources of Vitamin A to support healthy development.
Preventing Vitamin A Deficiency
Preventing Vitamin A deficiency requires a multifaceted approach that includes dietary changes, supplementation, and public health initiatives. By understanding the strategies for prevention, individuals and communities can work towards reducing the prevalence of this deficiency.
Dietary Recommendations
A balanced diet rich in Vitamin A is the cornerstone of prevention. Consuming a variety of foods that provide both preformed Vitamin A and provitamin A carotenoids is essential. Incorporating liver, dairy products, and fish oils can boost preformed Vitamin A intake. Additionally, colorful fruits and vegetables like carrots, sweet potatoes, and leafy greens are excellent sources of carotenoids. A diverse diet not only helps prevent deficiency but also promotes overall health.
Supplementation Guidelines
In areas where dietary sources are insufficient, Vitamin A supplementation can be a valuable preventive measure. Health organizations often recommend supplements for at-risk populations, such as young children and pregnant women. These supplements can help bridge the nutritional gap and prevent deficiency-related health issues. It’s important to follow recommended dosages to avoid the risk of toxicity, as excessive intake of Vitamin A can be harmful.
Public Health Initiatives
Public health programs play a crucial role in combating Vitamin A deficiency on a larger scale. Initiatives such as food fortification and community education can significantly impact the prevalence of deficiency. Fortifying staple foods with Vitamin A is a cost-effective strategy that has been successful in many regions. Additionally, educating communities about the importance of a balanced diet and the sources of Vitamin A can empower individuals to make informed dietary choices.
Treatment Options for Vitamin A Deficiency
Addressing Vitamin A deficiency involves a combination of medical interventions and lifestyle changes. Understanding the available treatment options can help individuals manage and overcome this nutritional deficiency.
Medical Interventions
For individuals with severe Vitamin A deficiency, medical interventions may be necessary. Healthcare providers may prescribe high-dose Vitamin A supplements to quickly restore adequate levels. These interventions are often crucial for preventing the progression of deficiency-related health issues. In some cases, additional treatments may be required to address specific symptoms or complications resulting from the deficiency.
Dietary Adjustments
Long-term management of Vitamin A deficiency involves making dietary adjustments to ensure sufficient intake of this nutrient. Incorporating foods rich in Vitamin A into daily meals can help maintain healthy levels. Regularly consuming a variety of animal and plant-based sources can provide a balanced intake of preformed Vitamin A and carotenoids. Consulting with a nutritionist or healthcare provider can offer personalized dietary recommendations to meet individual needs.
Monitoring and Follow-up Care
Ongoing monitoring and follow-up care are essential for individuals recovering from Vitamin A deficiency. Regular check-ups with healthcare providers can help track progress and ensure that Vitamin A levels remain within a healthy range. Monitoring is particularly important for at-risk populations, such as children and pregnant women, to prevent recurrence. By maintaining consistent follow-up care, individuals can effectively manage their nutritional health and prevent future deficiencies.
Global Efforts to Combat Vitamin A Deficiency
Addressing Vitamin A deficiency requires a coordinated global effort. Various programs and campaigns aim to reduce the prevalence of this deficiency and improve public health outcomes worldwide.
Programs and Campaigns
Numerous international organizations have implemented programs to combat Vitamin A deficiency. These initiatives often focus on food fortification, supplementation, and education. By working with local governments and communities, these programs aim to increase access to Vitamin A-rich foods and supplements. Collaborative efforts between governments, NGOs, and health organizations are crucial for the success of these initiatives.
Success Stories from Around the World
Several countries have made significant progress in reducing Vitamin A deficiency through targeted interventions. For example, food fortification programs in countries like India and Bangladesh have led to substantial improvements in public health. These success stories highlight the effectiveness of coordinated efforts in addressing nutritional deficiencies. Sharing best practices and lessons learned from these initiatives can inspire similar efforts in other regions.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite the progress made, challenges remain in the fight against Vitamin A deficiency. Limited resources, logistical constraints, and cultural barriers can hinder the implementation of effective programs. Future efforts must focus on overcoming these challenges through innovative solutions and increased collaboration. Continued investment in research and development, as well as the adaptation of successful strategies to local contexts, will be essential for achieving long-term success in combating Vitamin A deficiency globally.
Understanding Vitamin A Deficiency and Its Health Implications
What is the primary disease caused by a lack of Vitamin A?
The primary disease caused by a lack of Vitamin A is night blindness, which can progress to complete blindness if the deficiency is not addressed.
How does Vitamin A deficiency lead to night blindness?
Vitamin A is crucial for the production of rhodopsin, a pigment in the retina that helps the eyes adapt to low-light conditions. A deficiency in Vitamin A impairs this process, leading to night blindness.
Are there other health issues associated with Vitamin A deficiency?
Yes, Vitamin A deficiency can also lead to an increased risk of infections, delayed growth in children, and skin issues such as hyperkeratosis.
Who is most at risk for Vitamin A deficiency?
Populations most at risk include young children, pregnant women, and individuals with malabsorption disorders or diets lacking in Vitamin A-rich foods.
What foods can help prevent Vitamin A deficiency?
Foods rich in Vitamin A include liver, fish oils, leafy green vegetables, orange and yellow vegetables, and dairy products. Consuming a balanced diet with these foods can help prevent deficiency.
How is Vitamin A deficiency diagnosed?
Vitamin A deficiency is typically diagnosed through a combination of clinical examination, dietary assessment, and blood tests to measure serum retinol levels.
What are the treatment options for Vitamin A deficiency?
Treatment options include dietary changes to increase Vitamin A intake, supplementation, and addressing any underlying health conditions that may contribute to the deficiency.