Understanding the Big 4 Nutrients
Have you ever wondered what fuels the intricate machine that is your body? The answer lies in nutrients, the essential compounds that power every cell and system. Among these, four stand out as particularly crucial. But what exactly makes these nutrients so vital, and how do they contribute to our well-being? Let’s delve into the world of nutrition to uncover the secrets behind these key players.
Imagine a world where your body functions at its peak, with energy levels soaring and health issues at bay. This isn’t just a dream; it’s a reality attainable through understanding and incorporating the right nutrients into your diet. These nutrients not only support growth and repair but also play a pivotal role in disease prevention. As you read on, you’ll discover how each of these nutrients contributes uniquely to your health, ensuring that your body operates like a well-oiled machine.
What Are Nutrients and Why Are They Important?
Nutrients are the building blocks of life, essential for maintaining health and vitality. They are categorized into macronutrients and micronutrients, each serving distinct functions. Macronutrients, which include proteins, carbohydrates, and fats, provide energy and structure, while micronutrients such as vitamins and minerals support various biochemical processes. Without these vital compounds, our bodies would struggle to perform even the most basic functions.
The Role of Nutrients in Overall Health
The significance of nutrients extends beyond mere survival. They are instrumental in promoting growth, repairing tissues, and bolstering the immune system. A balanced intake of nutrients can prevent chronic diseases, enhance cognitive function, and improve mood. By understanding the role of each nutrient, we can tailor our diets to meet our individual health needs, ensuring longevity and quality of life.
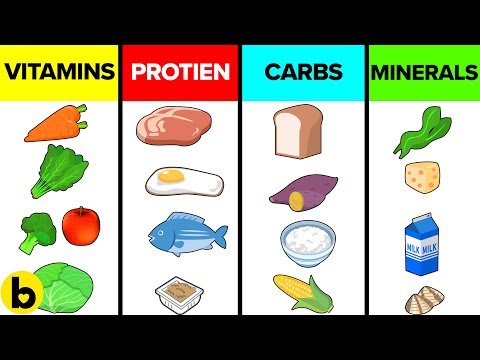
How to Identify the Big 4 Nutrients
The “Big 4” nutrients refer to proteins, carbohydrates, fats, and vitamins, each indispensable in its own right. Identifying these nutrients involves understanding their sources and functions. Proteins are found in meats, beans, and nuts; carbohydrates in grains and fruits; fats in oils and fish; and vitamins in a variety of fruits and vegetables. By recognizing these sources, we can make informed dietary choices that support optimal health.
Protein: The Building Block of Life
Proteins are often hailed as the body’s construction workers, responsible for building and repairing tissues. They are composed of amino acids, which are crucial for muscle growth, enzyme production, and hormone regulation. Without adequate protein intake, the body cannot maintain its structural integrity or perform essential functions.
Sources of High-Quality Protein
High-quality proteins are those that provide all essential amino acids in sufficient quantities. Animal sources such as chicken, fish, and eggs are considered complete proteins, while plant-based sources like quinoa and soy also offer comprehensive amino acid profiles. Incorporating a variety of these sources ensures that the body receives the necessary building blocks for optimal function.
Benefits of Protein for Muscle Growth and Repair
Protein is indispensable for muscle growth and repair, particularly for athletes and those engaged in regular physical activity. It aids in the recovery of muscle fibers damaged during exercise, promoting strength and endurance. Furthermore, a protein-rich diet can enhance metabolic rate, aiding in weight management and overall health.
How Much Protein Do You Really Need?
The amount of protein required varies based on age, activity level, and health goals. Generally, it is recommended that adults consume 0.8 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight. However, athletes and those with higher physical demands may require more. Consulting with a nutritionist can help determine the appropriate intake for individual needs.
Carbohydrates: Your Body’s Energy Source
Carbohydrates are the body’s primary energy source, fueling everything from daily activities to intense workouts. They are broken down into glucose, which is used by cells for energy. Despite their importance, carbohydrates often receive a bad rap, but understanding their role can help dispel myths and promote a balanced diet.
Simple vs. Complex Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are classified into simple and complex types. Simple carbohydrates, found in sugars and processed foods, provide quick energy but can lead to spikes in blood sugar. In contrast, complex carbohydrates, found in whole grains and vegetables, offer sustained energy and are rich in fiber, supporting digestive health.
The Importance of Fiber in Your Diet
Fiber, a type of carbohydrate, is crucial for maintaining digestive health. It aids in regulating bowel movements, lowering cholesterol levels, and controlling blood sugar. A diet rich in fiber can also promote satiety, helping with weight management. Foods like oats, beans, and fruits are excellent sources of dietary fiber.
Managing Carbohydrate Intake for Optimal Health
Balancing carbohydrate intake is essential for maintaining energy levels and preventing chronic diseases. Opting for whole, unprocessed sources and moderating portion sizes can help manage blood sugar levels and support overall health. Incorporating a variety of carbohydrate sources ensures a well-rounded diet that meets the body’s energy needs.
Fats: Essential for Brain and Heart Health
Fats are often misunderstood, yet they play a crucial role in supporting brain and heart health. They are involved in hormone production, nutrient absorption, and cell membrane integrity. Distinguishing between different types of fats can help us make healthier dietary choices.
Types of Fats: Good vs. Bad
Fats are categorized into saturated, unsaturated, and trans fats. Unsaturated fats, found in olive oil and avocados, are beneficial for heart health, while saturated fats, present in red meat and dairy, should be consumed in moderation. Trans fats, often found in processed foods, are harmful and should be avoided. Understanding these distinctions can guide us in making healthier dietary decisions.
The Role of Omega-3 and Omega-6 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids are essential fats that the body cannot produce on its own. Omega-3s, found in fish and flaxseeds, have anti-inflammatory properties and support heart health. Omega-6s, present in vegetable oils, are also important but should be balanced with omega-3 intake to prevent inflammation. Incorporating these fatty acids into the diet is vital for maintaining overall health.
How to Incorporate Healthy Fats into Your Diet
Incorporating healthy fats into your diet involves choosing sources rich in unsaturated fats and omega-3s. Cooking with olive oil, snacking on nuts, and consuming fatty fish like salmon can provide these essential nutrients. By prioritizing healthy fats, we can support brain function, reduce inflammation, and promote heart health.
Vitamins: The Micronutrient Powerhouses
Vitamins are micronutrients that, although required in small amounts, are vital for numerous bodily functions. They play roles in energy production, immune support, and bone health. A diet lacking in these essential compounds can lead to deficiencies and health issues.
Essential Vitamins for Daily Health
Vitamins are divided into two categories: water-soluble and fat-soluble. Water-soluble vitamins, such as vitamin C and the B-complex group, must be consumed regularly as they are not stored in the body. Fat-soluble vitamins, including vitamins A, D, E, and K, are stored in fatty tissues and the liver. Ensuring a varied diet can help meet daily vitamin requirements.
The Impact of Vitamin Deficiencies
Vitamin deficiencies can have significant health consequences. For instance, a lack of vitamin D can lead to weakened bones, while insufficient vitamin C can result in scurvy. Recognizing the signs of deficiencies and addressing them through diet or supplements is crucial for maintaining health.
Best Food Sources for Key Vitamins
Each vitamin has specific food sources that can help meet daily needs. Citrus fruits are rich in vitamin C, while leafy greens provide vitamin K. Dairy products offer vitamin D, and nuts are a good source of vitamin E. By incorporating a diverse range of foods, we can ensure adequate vitamin intake and support overall well-being.
Minerals: Supporting Vital Bodily Functions
Minerals are crucial for maintaining a variety of bodily functions, from bone health to nerve transmission. They are categorized into major minerals and trace minerals, each playing distinct roles in the body. Understanding their importance can help us make informed dietary choices.
Major Minerals vs. Trace Minerals
Major minerals, such as calcium, potassium, and sodium, are required in larger amounts and are vital for maintaining fluid balance and bone structure. Trace minerals, including iron, zinc, and selenium, are needed in smaller quantities but are equally important for processes like oxygen transport and immune function. Balancing these minerals is essential for optimal health.
The Importance of Calcium, Iron, and Magnesium
Calcium is essential for strong bones and teeth, while iron is crucial for oxygen transport in the blood. Magnesium plays a role in over 300 enzymatic reactions, including energy production and muscle function. Ensuring adequate intake of these minerals can prevent deficiencies and support overall health.
How to Ensure Adequate Mineral Intake
To maintain sufficient mineral levels, it is important to consume a varied diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains. Dairy products are excellent sources of calcium, while red meat and legumes provide iron. Nuts and seeds are rich in magnesium. Incorporating these foods into your daily meals can help meet your mineral needs.
Balancing the Big 4 Nutrients in Your Diet
Achieving a balanced diet involves understanding the roles of the big four nutrients and how they interact. By creating a nutrient-dense meal plan, we can ensure that our bodies receive the necessary components for optimal function.
Creating a Nutrient-Dense Meal Plan
A nutrient-dense meal plan focuses on whole, unprocessed foods that provide a variety of nutrients. Incorporating lean proteins, whole grains, healthy fats, and a rainbow of fruits and vegetables can help achieve this balance. Planning meals ahead can ensure that you meet your nutritional goals.
Tips for Maintaining Nutritional Balance
Maintaining nutritional balance requires mindfulness and intentionality. Prioritize whole foods over processed options, and pay attention to portion sizes. Incorporate a variety of food groups in each meal to ensure a comprehensive intake of nutrients. Listening to your body’s hunger cues can also guide you in maintaining balance.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Nutrient Intake
One common mistake is over-relying on one nutrient group while neglecting others. For example, consuming too many carbohydrates without sufficient protein can lead to imbalances. Additionally, avoiding fats entirely can deprive the body of essential fatty acids. Being aware of these pitfalls can help maintain a balanced diet.
The Future of Nutrition: Trends and Innovations
The field of nutrition is constantly evolving, with new trends and innovations shaping the way we approach our diets. Understanding these developments can help us make informed choices and embrace a healthier lifestyle.
Advances in Nutritional Science
Recent advances in nutritional science have shed light on the complex interactions between nutrients and health. Research has highlighted the importance of gut health, the role of antioxidants, and the impact of diet on mental health. Staying informed about these discoveries can empower us to make better dietary choices.
Personalized Nutrition and Its Benefits
Personalized nutrition tailors dietary recommendations to an individual’s unique genetic makeup, lifestyle, and health goals. This approach recognizes that one size does not fit all when it comes to diet. By considering personal factors, we can optimize our nutrient intake and improve health outcomes. Embracing personalized nutrition can lead to more effective and sustainable dietary changes.
The Role of Technology in Nutrient Tracking
Technology has revolutionized the way we track and manage our nutrient intake. Apps and wearable devices can monitor dietary habits, provide personalized recommendations, and help set and achieve nutrition goals. Utilizing these tools can enhance our understanding of our dietary patterns and support healthier choices.
In conclusion, understanding and balancing the big four nutrients—proteins, carbohydrates, fats, and vitamins—are crucial for maintaining health and vitality. By staying informed about the latest trends and innovations in nutrition, we can make educated choices that support our well-being and enhance our quality of life. Embracing a holistic approach to nutrition can empower us to lead healthier, more fulfilling lives.
Understanding the Big 4 Nutrients: Essential Elements for Health
What are the Big 4 Nutrients and why are they important?
The Big 4 Nutrients refer to carbohydrates, proteins, fats, and vitamins. These essential nutrients play a crucial role in maintaining overall health by providing energy, supporting bodily functions, and aiding in growth and repair.
How do carbohydrates function as one of the Big 4 Nutrients?
Carbohydrates are the body’s primary source of energy. They are broken down into glucose, which fuels your brain, muscles, and other vital organs. Including complex carbohydrates in your diet can help maintain steady energy levels throughout the day.
Why are proteins considered a vital nutrient among the Big 4?
Proteins are essential for building and repairing tissues, producing enzymes and hormones, and supporting immune function. They are made up of amino acids, which are the building blocks necessary for various bodily processes.
What role do fats play in the Big 4 Nutrients?
Fats are a concentrated source of energy and are crucial for absorbing fat-soluble vitamins, protecting organs, and maintaining cell membranes. Healthy fats, such as those found in avocados and nuts, are important for heart health and brain function.
How do vitamins fit into the Big 4 Nutrients?
Vitamins are organic compounds that are vital for various metabolic processes. They support immune function, bone health, and wound healing, among other roles. Each vitamin has a unique function, making a balanced intake essential for optimal health.
Can you get all the Big 4 Nutrients from a single food source?
While no single food provides all the Big 4 Nutrients in sufficient amounts, a balanced diet that includes a variety of foods can help ensure you receive adequate levels of each nutrient. Incorporating fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats is key.
What are some tips for balancing the Big 4 Nutrients in your diet?
To balance the Big 4 Nutrients, focus on portion control and variety. Aim to fill half your plate with fruits and vegetables, choose whole grains, include lean protein sources, and opt for healthy fats. Consulting a nutritionist can also provide personalized guidance.