Understanding the Basics of Nutrition Studies
Have you ever wondered how scientists determine the impact of different foods on our health? The field of nutrition is vast and complex, yet it is crucial for understanding how our dietary choices affect our well-being. Nutrition studies are the backbone of dietary guidelines, helping to unravel the intricate relationship between diet and health. These studies are essential for developing effective public health strategies and personal dietary recommendations. By exploring the two main types of studies in nutrition, we can gain a deeper appreciation of how these investigations shape our understanding of food and health.
Nutrition research is not just about counting calories or tracking nutrients; it is a scientific endeavor that involves meticulous planning and execution. Researchers employ various methodologies to gather data and draw meaningful conclusions. The insights gained from these studies are invaluable, influencing everything from food labeling to government policy. As we delve into the world of nutrition studies, we will explore how these investigations are conducted and the significance they hold in our everyday lives.
Defining Nutrition Studies
At the core of nutrition research are two primary methodologies: observational and experimental studies. Each approach offers unique insights into dietary patterns and their health implications. Observational studies involve monitoring and analyzing dietary habits without altering them, while experimental studies involve controlled interventions to assess specific outcomes. Understanding the nuances of these methodologies is crucial for interpreting research findings and applying them to real-world scenarios.
Importance of Nutrition Research
Nutrition research plays a pivotal role in shaping public health policies and dietary guidelines. By identifying the links between diet and disease, these studies provide evidence-based recommendations that promote healthier lifestyles. Without rigorous research, our understanding of nutrition would be limited, potentially leading to misguided dietary advice. As we navigate the complexities of nutrition science, it is essential to appreciate the meticulous work that underpins our knowledge of food and health.
Observational Studies: An Overview
Observational studies are a cornerstone of nutrition research, offering valuable insights into dietary patterns and their health outcomes. These studies involve monitoring participants’ diets and health over time without altering their behavior. By observing natural dietary habits, researchers can identify associations between specific foods and health conditions. This approach is particularly useful for studying long-term dietary effects and large populations.
Types of Observational Studies
Observational studies can be categorized into several types, each with its unique methodology and focus. Cohort studies follow a group of individuals over time, collecting data on their dietary habits and health outcomes. Case-control studies compare individuals with a specific health condition to those without, examining their dietary histories for potential risk factors. Cross-sectional studies provide a snapshot of dietary patterns and health at a single point in time, offering insights into population-wide trends.
Advantages of Observational Studies
One of the primary advantages of observational studies is their ability to capture real-world dietary behaviors. By studying natural eating patterns, researchers can identify potential risk factors and protective dietary components. These studies are particularly valuable for generating hypotheses that can be tested in experimental settings. Additionally, observational studies can accommodate large sample sizes, enhancing the generalizability of their findings.
Experimental Studies: A Closer Look
Experimental studies are a fundamental component of nutrition research, providing robust evidence for causal relationships between diet and health. These studies involve controlled interventions, where researchers manipulate dietary variables to assess their impact on health outcomes. By controlling for confounding factors, experimental studies offer a high level of scientific rigor and reliability.
Types of Experimental Studies
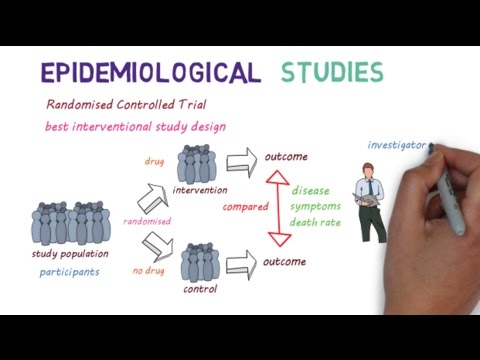
Experimental studies can be divided into several categories, each with its specific design and purpose. Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) are considered the gold standard, involving the random assignment of participants to intervention or control groups. This design minimizes bias and allows for precise comparisons. Other types of experimental studies include crossover trials, where participants receive multiple interventions in a specific order, and factorial trials, which assess the effects of multiple interventions simultaneously.
Benefits of Experimental Studies
Experimental studies offer several advantages over observational approaches. By controlling for external variables, these studies provide strong evidence for cause-and-effect relationships. This level of control allows researchers to isolate the effects of specific dietary components, offering precise insights into their health impacts. Additionally, experimental studies can be tailored to investigate specific research questions, making them highly versatile and informative.
Comparing Observational and Experimental Studies
Understanding the differences between observational and experimental studies is crucial for interpreting nutrition research. While both methodologies offer valuable insights, they differ in their design, objectives, and applications. By comparing these approaches, we can better appreciate their strengths and limitations in the context of nutrition science.
Key Differences
The primary distinction between observational and experimental studies lies in their approach to data collection. Observational studies rely on natural dietary behaviors, while experimental studies involve controlled interventions. This fundamental difference impacts the types of conclusions that can be drawn from each study. Observational studies are well-suited for identifying associations, while experimental studies provide evidence for causal relationships.
When to Use Each Type
The choice between observational and experimental studies depends on the research question and available resources. Observational studies are ideal for exploring broad dietary patterns and generating hypotheses for further investigation. These studies are particularly useful for examining long-term dietary effects and large populations. Experimental studies, on the other hand, are best suited for testing specific hypotheses and establishing causal relationships. By combining both approaches, researchers can gain a comprehensive understanding of nutrition and its impact on health.
The Role of Epidemiology in Nutrition Studies
Epidemiology is a critical component of nutrition research, providing the tools and methodologies needed to study dietary patterns and their health impacts. By applying epidemiological methods, researchers can identify trends, associations, and risk factors that inform public health strategies and dietary guidelines.
Epidemiological Methods
Epidemiological methods encompass a range of techniques used to study the distribution and determinants of health-related states in populations. These methods include statistical analyses, data collection, and study design, all of which are essential for conducting robust nutrition research. By employing these techniques, researchers can identify patterns and associations that inform public health interventions.
Impact on Public Health
The insights gained from epidemiological studies have a profound impact on public health, shaping dietary guidelines and informing policy decisions. By identifying dietary risk factors and protective components, these studies provide evidence-based recommendations that promote healthier lifestyles. The findings from epidemiological research are instrumental in developing effective public health strategies and interventions. As we continue to explore the role of epidemiology in nutrition studies, it is essential to recognize its contributions to our understanding of diet and health.
Challenges in Conducting Nutrition Studies
Conducting nutrition research presents numerous challenges, ranging from methodological complexities to practical constraints. These obstacles can impact the reliability and validity of study findings, making it essential to address them effectively. By understanding these challenges, researchers can develop innovative solutions that enhance the quality of nutrition studies.
Common Obstacles
One of the primary challenges in nutrition research is the difficulty in accurately measuring dietary intake. Self-reported data, often used in studies, can be prone to bias and inaccuracies. Additionally, the long-term nature of many nutrition studies requires sustained participant engagement, which can be difficult to maintain. Another significant obstacle is the influence of confounding variables, which can obscure the true relationship between diet and health outcomes. These challenges necessitate careful study design and data analysis to ensure robust findings.
Solutions and Innovations
To overcome these challenges, researchers are employing a range of innovative strategies. The use of technology, such as mobile apps and wearable devices, is enhancing the accuracy of dietary assessments. These tools allow for real-time data collection and reduce reliance on self-reported information. Additionally, advanced statistical techniques are being used to control for confounding variables and improve the precision of study results. Collaborative research efforts and large-scale cohort studies are also providing valuable insights into complex dietary patterns and health outcomes. By embracing these innovations, nutrition researchers can address common obstacles and advance the field.
The Impact of Nutrition Studies on Dietary Guidelines
Nutrition studies play a crucial role in shaping dietary guidelines, providing the evidence base for recommendations that promote public health. These guidelines are informed by a comprehensive analysis of research findings, ensuring that they reflect the latest scientific understanding of diet and health.
How Studies Shape Guidelines
The process of developing dietary guidelines involves a thorough review of nutrition research, including both observational and experimental studies. By synthesizing evidence from multiple studies, experts can identify key dietary patterns and nutrients that influence health outcomes. This evidence is then used to formulate recommendations that aim to reduce the risk of chronic diseases and promote overall well-being. The iterative nature of this process ensures that guidelines are continually updated to reflect new research findings and emerging trends in nutrition science.
Recent Changes in Dietary Recommendations
Recent updates to dietary guidelines have been influenced by a growing body of research highlighting the importance of whole foods and plant-based diets. Studies have shown that diets rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats can reduce the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease and diabetes. As a result, recent guidelines emphasize the consumption of nutrient-dense foods and the reduction of added sugars and saturated fats. These changes reflect a shift towards a more holistic approach to nutrition, recognizing the complex interplay between diet and health.
Future Trends in Nutrition Research
As the field of nutrition science continues to evolve, researchers are exploring new frontiers and embracing emerging technologies to enhance their understanding of diet and health. These advancements hold the potential to revolutionize nutrition research and inform future dietary guidelines.
Emerging Technologies
The integration of technology into nutrition research is paving the way for more precise and personalized dietary recommendations. Advances in genomics and metabolomics are allowing researchers to explore the interactions between diet and genetic factors, leading to a deeper understanding of individual nutritional needs. Additionally, machine learning and artificial intelligence are being used to analyze large datasets, uncovering patterns and associations that were previously inaccessible. These technologies are transforming the landscape of nutrition research, offering new insights into the complex relationship between diet and health.
Areas for Further Exploration
Several areas of nutrition research are poised for further exploration, including the impact of gut microbiota on health and the role of nutrition in mental well-being. Emerging evidence suggests that the composition of gut bacteria can influence metabolic health and disease risk, highlighting the need for more research in this area. Additionally, the relationship between diet and mental health is gaining attention, with studies suggesting that certain dietary patterns may support cognitive function and emotional well-being. By investigating these areas, researchers can expand our understanding of nutrition and its far-reaching impacts on health.
In conclusion, nutrition studies are a vital component of public health research, providing the evidence needed to develop effective dietary guidelines and interventions. By understanding the two main types of studies in nutrition, researchers can harness their strengths and address their limitations to advance the field. As new technologies and research areas emerge, the future of nutrition science holds great promise for improving health outcomes and enhancing our understanding of diet and well-being.
Understanding the Core Types of Nutrition Studies: A Comprehensive FAQ
What are the two main types of studies in nutrition?
The two primary types of studies in nutrition are observational studies and experimental studies. Observational studies involve monitoring and analyzing dietary patterns and health outcomes without intervention, while experimental studies involve controlled trials where variables are manipulated to observe effects on health.
How do observational studies contribute to nutrition research?
Observational studies help identify correlations between dietary habits and health outcomes by examining large populations over time. They provide valuable insights into potential risk factors and dietary patterns that may influence health, although they cannot establish causation.
What are the advantages of experimental studies in nutrition?
Experimental studies, such as randomized controlled trials (RCTs), allow researchers to establish cause-and-effect relationships by controlling variables and using randomization. This method provides strong evidence for the effects of specific dietary interventions on health outcomes.
Can observational studies determine causation in nutrition?
No, observational studies cannot determine causation because they do not control for all variables. They can suggest associations and generate hypotheses, but experimental studies are needed to confirm causal relationships.
What are some common challenges faced in conducting nutrition studies?
Nutrition studies often face challenges such as participant adherence, accurate dietary reporting, and controlling for confounding variables. Additionally, the complexity of human diets and individual variability can make it difficult to isolate specific dietary effects.
Why is it important to consider both types of studies in nutrition research?
Considering both observational and experimental studies is crucial for a comprehensive understanding of nutrition. Observational studies provide broad insights and help identify trends, while experimental studies offer precise evidence of causality, together forming a robust evidence base for dietary guidelines and recommendations.